-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 26
Python Example IoT 1
This example shows how easily you can drive a RF Explorer IoT module using the Python library. This is a very simple, “Hello World” equivalent example to understand how RF Explorer Python library works.
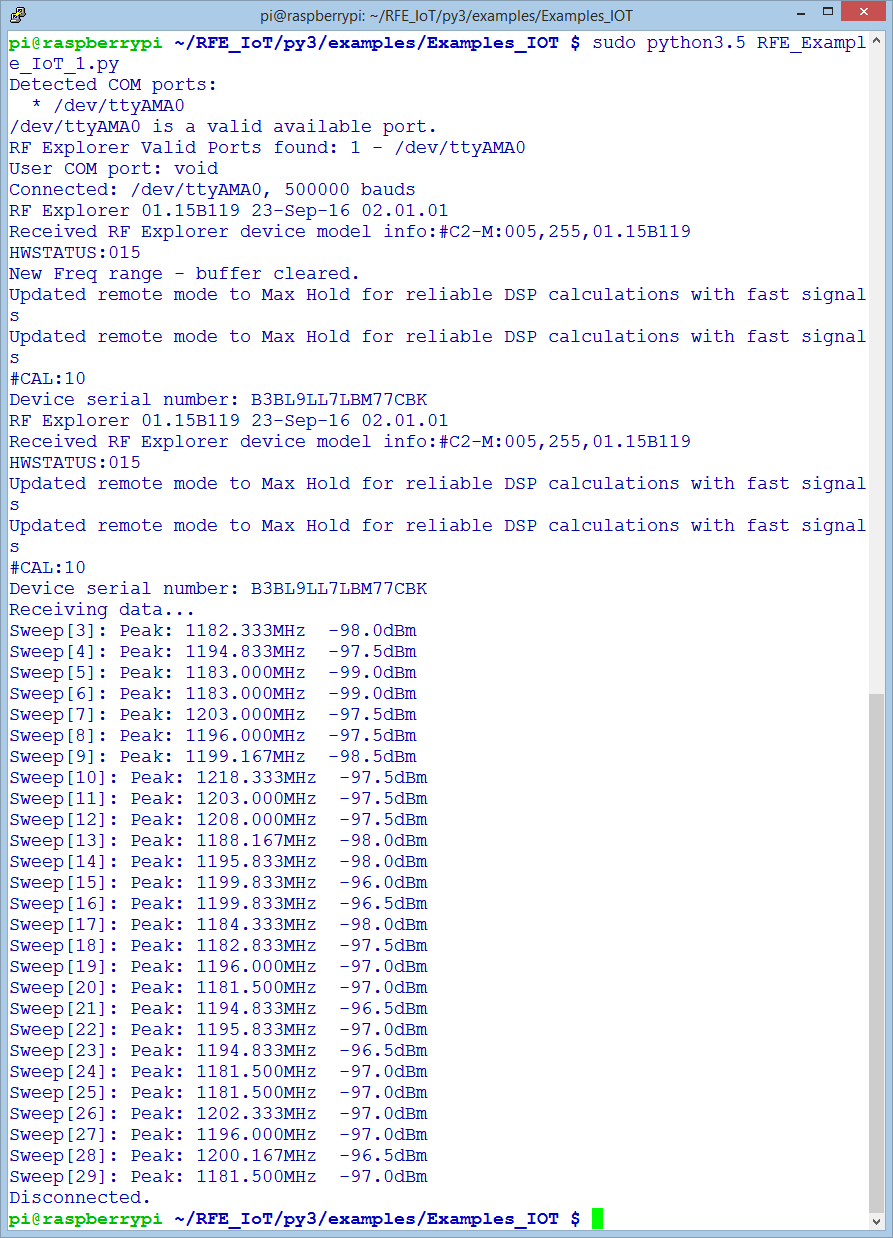
Initializes the RF module, then request configuration details and check for peak signal value in Amplitude and Frequency within the default RF scanning range.
It keeps scanning for 10 seconds then program automatically close.
- Use the official Raspberry Pi image from RF Explorer download page
- Install latest RF Explorer Python libraries - details here
- Download the example from GITHUB repository link
Open a terminal in your Raspberry Pi and run
sudo python3.5 RFE_Example_IoT_1.py
Note you must run all python code in Raspberry Pi as superuser, otherwise the internal Raspberry Pi digital pins cannot be updated as required. This is a specific requirement from Raspberry Pi drivers, not RF Explorer. If you forget to use sudo, you will get some error message like this: Error importing RPi.GPIO! This is probably because you need superuser privileges. You can achieve this by using 'sudo' to run your script
As depicted below, you will get automatic connection to the IoT board using /dev/ttyAMA0 UART from the Raspberry Pi.
- Firmware version embedded into the RF Explorer IoT module
- Active connection at 500,000 baud
- RF Explorer IoT Device serial number
- Receiving data scan, with 10 seconds activity displaying default range. For the sake of simplicity, this example does not change default settings defined as 1.180 – 1.220GHz.