You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.Dismiss alert
Copy file name to clipboardExpand all lines: docs/release-notes.md
+46-16Lines changed: 46 additions & 16 deletions
Display the source diff
Display the rich diff
Original file line number
Diff line number
Diff line change
@@ -2,23 +2,64 @@
2
2
3
3
This page shows features that have landed to kepler.gl in major versions. For a complete list of changes to kepler.gl including each minor version, please [visit the full change log](../CHANGELOG.md).
4
4
5
-
## 3.1
5
+
## 3.1.1
6
+
7
+
_Released march 10th, 2025_
8
+
9
+
### DuckDB
10
+
11
+
The DuckDB integration has been updated in response to feedback and requests, speeding up workflows for projects with local data. Notable changes include:
12
+
13
+
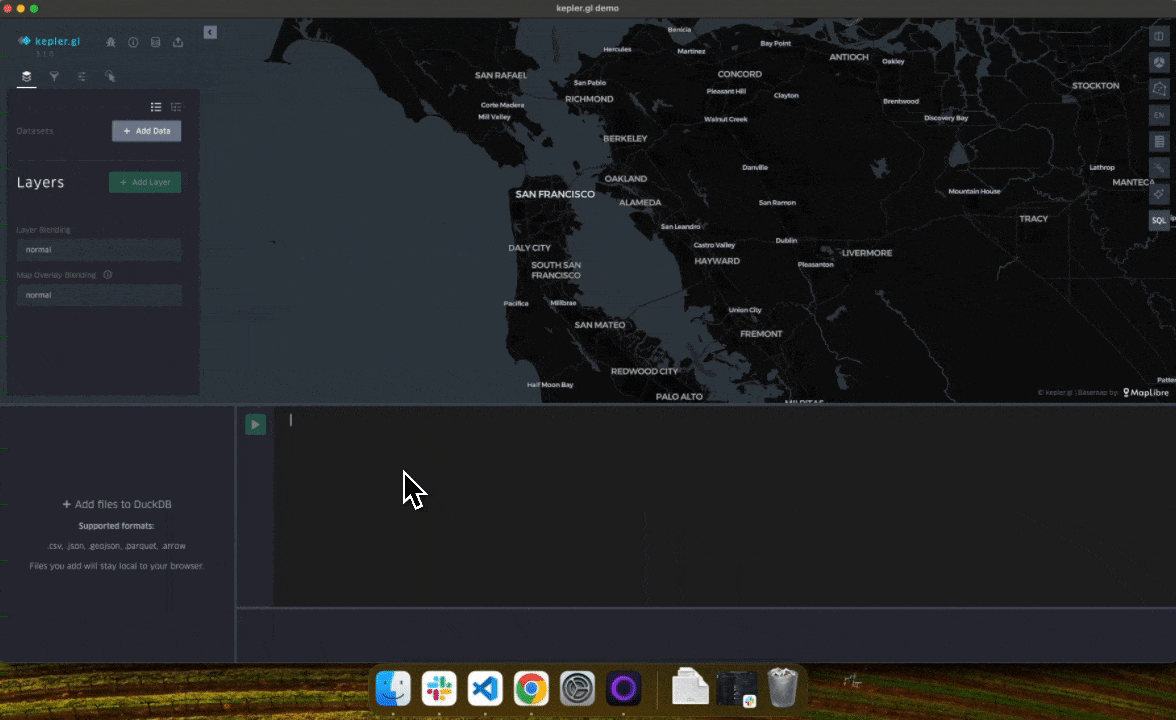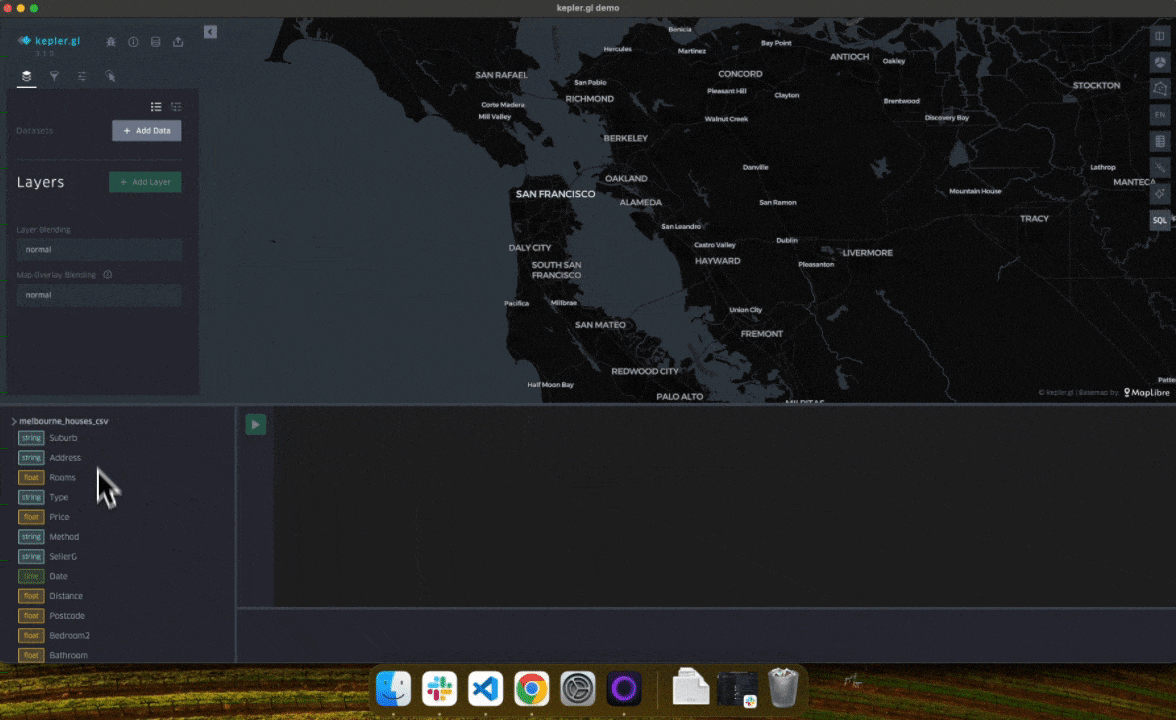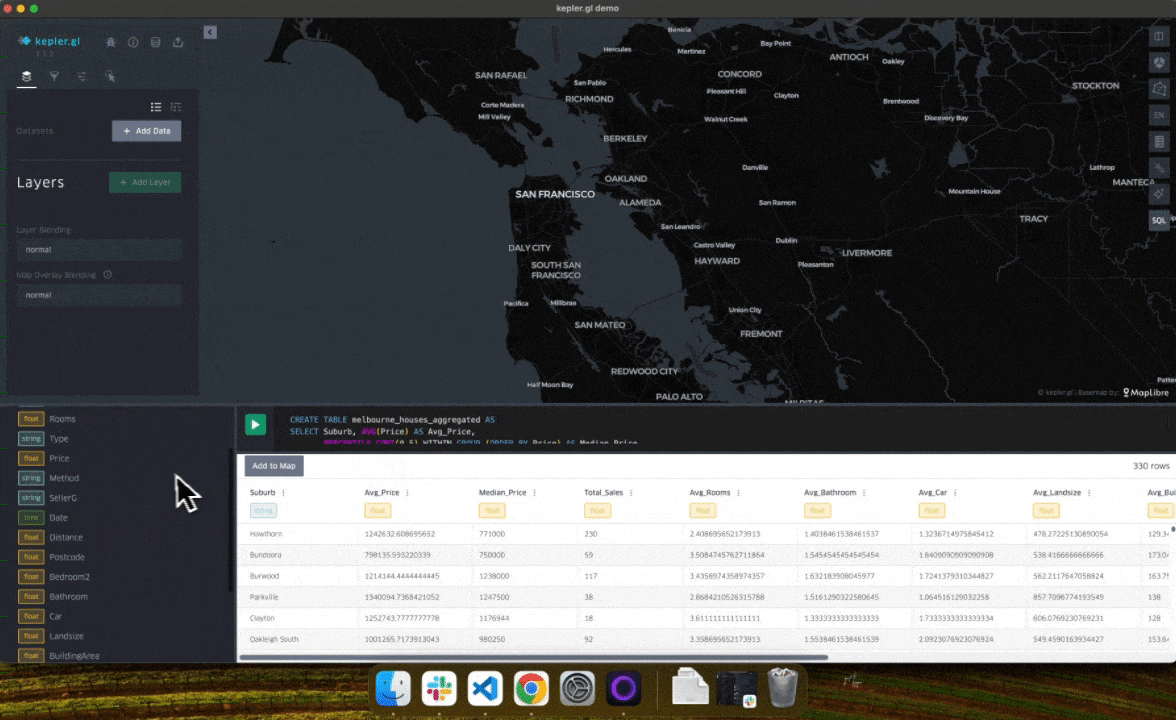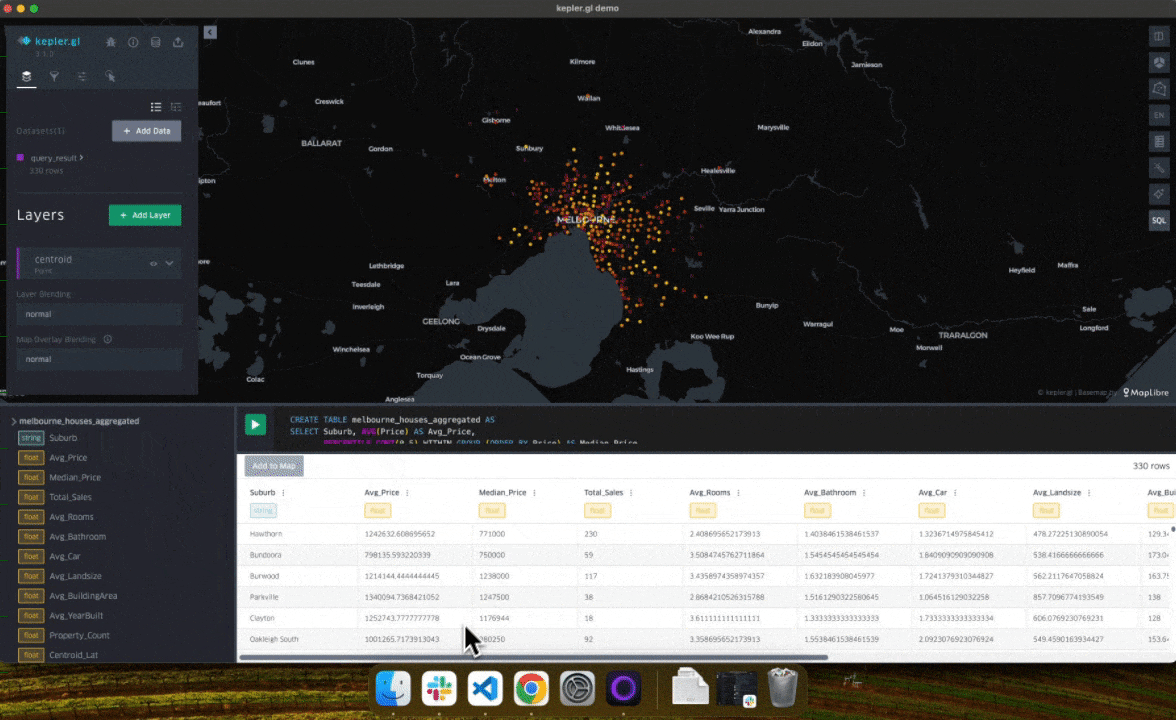
- Users can now drag and drop files directly in kepler.gl to create a DuckDB table.
14
+
- The schema panel now always updates when running a query.
15
+
- Improved handling of DuckDB column types.
16
+
17
+
18
+
19
+
### Vector Tiles
20
+
21
+
The Vector Tile layer has received a number of optimizations, bug fixes, and quality-of-life improvements. Notable changes include:
22
+
23
+
- For older tilesets without fields in the metadata file, kepler.gl now attempts to retrieve fields from the tile data.
24
+
- Automatically center the map to the tileset bounds.
25
+
- Fix for UI freezes during initial Tileset setup.
26
+
27
+
### More Bug Fixes
28
+
29
+
A number of bug fixes have been deployed in response to community feedback. The most notable bug fixes are listed below, but you can view a full list of changes [in the full change log](../CHANGELOG.md).
30
+
31
+
- Fix for geocoder coordinates, allowing users to enter coordinates directly.
32
+
- Fix for icon layers at higher zoom levels—icons now remain the same size.
33
+
- Fix for a broken section of the Icon Layer UI.
34
+
- Ensure the RangeBrush updates when the slider range changes.
35
+
- Transform binary buffers to hex WKB when saving to JSON/HTML maps.
36
+
- Improved logic for changing layer types.
37
+
- Support arrow text labels from non-string vector sources.
38
+
- Export GeoArrow columns to CSV as GeoJSON.
39
+
- Restore support for string WKB data; save binary WKB as hex WKB.
40
+
- AI Assistant now sends messages to 127.0.0.1 instead of a remote Ollama URL.
41
+
- Fix for disappearing heatmaps when rendering black or duplicate colors.
42
+
- Fix for point column suggestions not working.
43
+
- Fix for crashes in GeoJSON and Trip layers when no data is present.
44
+
- Fix for the "Save Map" action when using the FSQ provider (overwrite logic).
45
+
- FSQ storage provider now prompts for login instead of auto-login after logout.
46
+
47
+
## 3.1
6
48
7
49
_Released January 29th, 2025_
8
50
9
-
### Vector Tiles
51
+
### Vector Tiles
10
52
11
53
The new [Vector Tile layer](/docs/user-guides/c-types-of-layers/vector.md) allows the map to dynamically retrieve data based on the user's viewport and zoom level. This initial release supports both Mapbox Vector Tiles and PMTiles.
12
54
13
55
By leveraging the efficiency of vector tiles, users can visualize complex, large-scale datasets without compromising performance, making it easier to explore and analyze geospatial data.
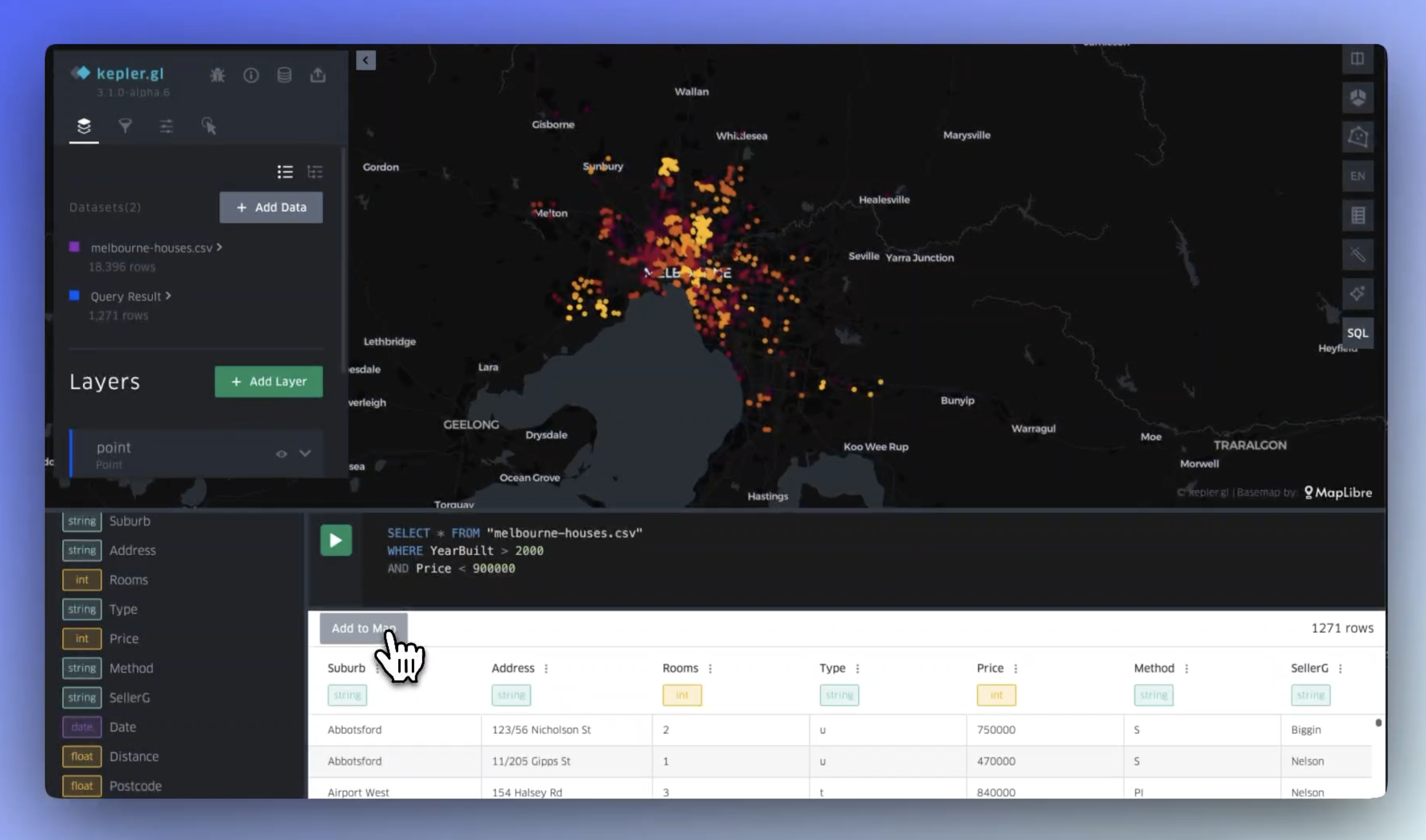
Leverage DuckDB directly within kepler.gl your geospatial projects with big data. Write and execute SQL queries to perform custom analyses, visualizing the results on your map.
21
-
62
+
22
63
DuckDB enables in-browser data processing, allowing you to work with large datasets without the need for external infrastructure.
23
64
24
65
@@ -33,40 +74,29 @@ Kepler’s AI assistant can edit the map, including filters, base map customizat
33
74
34
75
Mapbox and MapLibre base maps are now simultaneously supported.
35
76
36
-
37
77
### Color Scale Improvements
38
78
39
79
Custom color scale is now supported in categorial/ordinal fields, aggregate layers, and other layer components. In addition, custom breaks are now supported within the color scales.
40
80
41
-
42
81
### Value Formatting
43
82
44
83
Formatting for numeric values (e.g. 10,000 can be formatted 10k, $10,000.00, etc; .42 can be formatted as 42%).
45
84
46
-
47
85
### Animation Improvements
48
86
49
87
Includes various updates to the user interface for animation (for both time filters and the trip layer). You may also sync the layers (such as the trip layer) with filters, and conversely sync filters with the layer.
50
88
51
-
52
89
### Legend Improvements
53
90
54
91
The legend is now both movable and resizable, supports the editing of legend values, and offers a scale for radius scaling.
55
92
56
-
57
93
### Various Layer Improvements
58
94
59
-
A number of improvements to layers, including:
95
+
A number of improvements to layers, including:
60
96
61
97
- Zoom to layer button lets users center their viewport on the layer’s data
62
98
- Point layer now supports geojson
63
99
- Arc layer supports creation from h3
64
100
- A vast number of other layer improvements
65
101
66
102
This release also includes a wide range of bug fixes and performance improvements, which can be viewed in the [full change log.](../CHANGELOG.md)
Copy file name to clipboardExpand all lines: docs/user-guides/ai-assistant.md
+13-15Lines changed: 13 additions & 15 deletions
Display the source diff
Display the rich diff
Original file line number
Diff line number
Diff line change
@@ -8,30 +8,29 @@ The AI assistant in Kepler.gl is not only a LLM based chatbot, it is engineered
8
8
9
9
Your conversations can be advanced: `Create a geojson layer using population with quantile color scale and update its colors inspired by Van Gogh's Starry Night`. Or: `Check the correlation between temperature and precipitation in the dataset`.
10
10
11
-
12
11
## Supported Providers
13
12
14
13
The following providers and models are currently supported.
15
14
16
15
> Note: we are working on feature to allow users specify their own providers, models and base URL.
Before initating the AI assistant, the following parameters are required. A temperature and Top P are selected for you; however, you will need to provide an API key for a remote model, and a base URL for local models.
|**Temperature**| Controls the randomness of the model's output. Range: `0-2`, Default: `1`. Lower values make responses more focused and deterministic. |
32
31
|**Top P**| Controls the diversity of the output by limiting the cumulative probability of token selection. Range: `0-1`, Default: `0.8`. |
33
-
|**API Key**| Required for OpenAI (`gpt` models) and Google (`gemini` models). |
34
-
|**Base URL**| Required for Ollama (`localhost:11434` or another specified base URL). |
32
+
|**API Key**| Required for OpenAI (`gpt` models) and Google (`gemini` models).|
33
+
|**Base URL**| Required for Ollama (`localhost:11434` or another specified base URL).|
35
34
36
35
## Built-in Features
37
36
@@ -42,7 +41,7 @@ Before initating the AI assistant, the following parameters are required. A temp
42
41
43
42
This feature enables users to capture a screenshot anywhere within kepler.gl application and ask questions about the screenshot.
44
43
45
-
For example, users can take a screenshot of the map (or partial of the map) and ask questions about the map e.g. *`how many counties are in this screenshot`*, or take a screenshot of the layer configuration panel and ask questions about how to use it, e.g. *`How can I adjust the opacity`*. Users can even take a screenshot of the plots in the chat panel and ask questions about the plots e.g. *`Can you give me a summary of the plot?`*.
44
+
For example, users can take a screenshot of the map (or partial of the map) and ask questions about the map e.g. _`how many counties are in this screenshot`_, or take a screenshot of the layer configuration panel and ask questions about how to use it, e.g. _`How can I adjust the opacity`_. Users can even take a screenshot of the plots in the chat panel and ask questions about the plots e.g. _`Can you give me a summary of the plot?`_.
46
45
47
46

48
47
@@ -100,11 +99,11 @@ The current supported actions are:
100
99
- Spatial Analysis:
101
100
- Spatial join two datasets (e.g. count points and polygons).
102
101
103
-
> Note: to see our plan to add more actions to the AI assistant, please check out this [Kepler.gl RFC]([https://github.com/kepler-gl/kepler.gl/issues/4689](https://github.com/keplergl/kepler.gl/discussions/2843)) and the [integration of GeoDa with Kepler.gl]([text](https://github.com/GeoDaCenter/openassistant/wiki/Integration-Kepler.gl---GeoDaLib))
102
+
> Note: to see our plan to add more actions to the AI assistant, please check out this [Kepler.gl RFC](<[https://github.com/kepler-gl/kepler.gl/issues/4689](https://github.com/keplergl/kepler.gl/discussions/2843)>) and the [integration of GeoDa with Kepler.gl](<[text](https://github.com/GeoDaCenter/openassistant/wiki/Integration-Kepler.gl---GeoDaLib)>)
104
103
105
104
Users can simply describe what they want to accomplish in plain text, and the AI Assistant will invoke the appropriate function with the correct parameters that your application can execute. The LLM will identify if the question can be answered by using one or multiple function tools, and the LLM will ask the user to confirm the parameters of each function call.
106
105
107
-
> *Can you classify the data of the variable "population" using natural breaks and create a geojson layer using the breaks with colors inspired by Van Gogh's Starry Night.*
106
+
> _Can you classify the data of the variable "population" using natural breaks and create a geojson layer using the breaks with colors inspired by Van Gogh's Starry Night._
108
107
109
108
#### Plots
110
109
@@ -136,4 +135,3 @@ The regression details include:
136
135
This scatter plot can help users to explore the relationship between two variables, and explore the heterogeneity of the data by selecting different points.
| Color Based On | The field to base the fill color on. |
26
+
| Color Scale | The color scale and palette for the fill color. |
28
27
| Dynamic Color | Enable to estimate color range and scale based on tiles selected for rendering. When panning the map, the color scale will update dynamically. |
29
-
| Opacity | The opacity of the fill color. 100 = fully opaque, 0 = fully transparent. |
28
+
| Opacity | The opacity of the fill color. 100 = fully opaque, 0 = fully transparent. |
30
29
31
30
## Stroke Color
32
31
@@ -59,10 +58,8 @@ Height settings for the Vector layer. Height is best viewed with the 3D viewing
> Note: This feature is currently undergoing development. Stay tuned for updates!
3
+
**This feature is currently undergoing development. Stay tuned for updates!**
4
4
5
5
The new SQL data explorer provides a DucKDB instance where you can use SQL to transform and add data to the map.
6
6
7
7

8
8
9
9
You will need local data (i.e. data upload for your machine) or data accessible via a remote URL.
10
10
11
-
Any dataset already added to kepler can be accessed via SQL editor by selecting it via its name in kepler. For instance, if your dataset is named `world-cities.csv`, you can select the entire dataset by writing `SELECT * FROM 'world-cities.csv'`.
11
+
Any dataset already added to kepler can be accessed via SQL editor by selecting it via its name in kepler. For instance, if your dataset is named `world-cities.csv`, you can select the entire dataset by writing `SELECT * FROM 'world-cities.csv'`.
12
12
13
13
The data does not need to be pre-loaded to kepler -- you may also select data remotely via SQL. The following example loads earthquake data from our sample data repository:
14
14
15
15
```
16
16
SELECT * FROM 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/keplergl/kepler.gl-data/refs/heads/master/earthquakes/data.csv'
17
17
```
18
18
19
-
20
19
Once you have a data selection you are satisfied with, click **Add to Map**. Your new dataset will be added to kepler. If you have a column that contains recognizable geography data, (i.e. lat/lng columns or polygon geometries), layers will automatically be created.
0 commit comments