Welcome to the Lung Cancer Classification project using Deep Learning. This repository is dedicated to developing robust deep learning models to classify CT scan images into various types of lung cancer. Utilizing state-of-the-art convolutional neural networks (CNNs), this project aims to improve the accuracy of early lung cancer detection, which is critical for effective treatment and patient outcomes.
Download the dataset used in this project here.
- Build Model Architecture
- Apply Almost 5 to 6 Models(ResNet50,VGG16,ResNet101, VGG19, DenseNet201, EfficientNetB4, MobileNetV2) using Transfer Learning🧠
- Select 3 Most Promising Models 🌟
- Fine Tuning These Models to Increase Accuracy 📈
The dataset consists of CT scans labeled into the following categories, which represent different types of lung cancer and normal conditions:
- Normal
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Adenocarcinoma
- Large Cell Carcinoma
The data is preprocessed to align image sizes and augment the dataset to ensure robustness and generalizability of the models.
using the shuffle function to randomly shuffle the order of my training data to ensure that the model does not learn patterns based on the order of the data. dataset have training, testing, validation folders. dataset is from kaggle
This model architecture is a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) designed for image classification, utilizing the TensorFlow Keras library. The model begins with an input layer that accepts images of shape (305, 430, 3). It then processes these images through a series of convolutional and pooling layers. The first convolutional layer has 8 filters with a 2x2 kernel, followed by a max-pooling layer with a 2x2 pool size. The second convolutional layer increases the filter count to 16, also with a 2x2 kernel and includes L2 regularization to prevent overfitting, followed by another max-pooling layer. A dropout layer with a 0.4 rate is included to further mitigate overfitting. The output from these layers is flattened into a 1D vector, which is fed into a dense layer with 300 units and ReLU activation. Another dropout layer with a 0.5 rate is applied before the final output layer, which has 4 units corresponding to the number of classes, with softmax activation for multi-class classification.
In this project, we explore several advanced CNN architectures known for their efficacy in image classification tasks:
- VGG19: Known for its simplicity and depth, which is effective in capturing intricate patterns in image data.
- ResNet50: Utilizes residual connections to enable training of deeper neural network architectures without performance degradation.
- DenseNet201: Features dense connections between layers to enhance feature propagation and reuse, making it highly efficient.
- EfficientNetB4: Balances model scaling across depth, width, and resolution, leading to improved efficiency and accuracy.
- ResNet50 86% accuray on test data 📉
- DenseNet201 88% on test data 📊
- EfficientNetB4 90% on test data 📈
- ResNet50 with train 99.5 🟢 validation 89 🟡 test 91.7 🔵
- DenseNet201 with train 100 🟢 validation 94.5 🟢 test 90 🟡
- EfficientNetB4 with train 99 🟢 validation 94.5 🟢 test 89.5 🟡
From results we can see that using both models argmax(ResNet + DenseNet) is more accurate rather than using only one of them
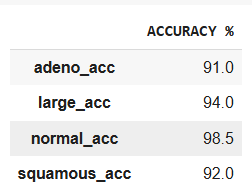
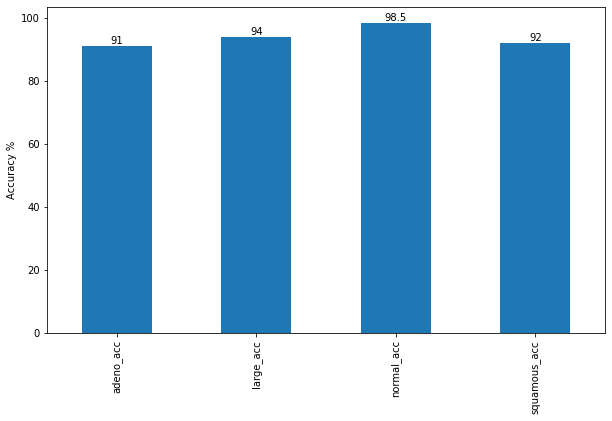
Below is the accuracy using Dataset images classes:
This project employs various technologies and libraries, primarily focused on Python for data science and machine learning:
- TensorFlow and Keras: For designing, training, and evaluating deep learning models.
- NumPy and Pandas: For efficient data manipulation and analysis.
- Matplotlib and Seaborn: For visualizing data and model performance metrics.
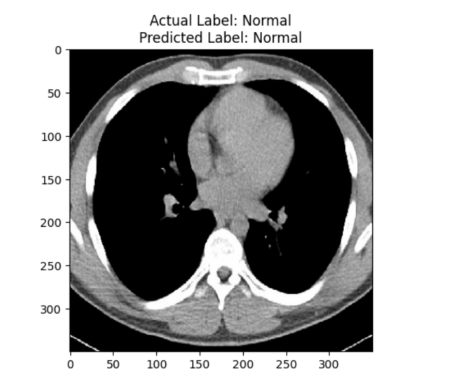
using final model